Appearance
place-object
The place-object component enables placing virtual objects in AR environments by tapping on detected real-world surfaces. It provides sophisticated control over how objects are positioned and oriented relative to the surface.
Props
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| heightRange | vec2 | { x: 0.3, y: 2.0 } | Min/max height range for valid placement (meters) |
| surfaceTypes | array | ["horizontal"] | Valid surface types: "horizontal", "wall", "ceiling" |
| distanceRange | vec2 | { x: 0.5, y: 5.0 } | Min/max distance from camera for valid placement |
| scale | number | 1.0 | Scale applied to the placed object |
| adjustOrientation | boolean | true | Whether to adjust object orientation based on surface type. The places object will keep a relative position to surface. |
| customRotation | vec3 | { x: 0, y: 0, z: 0 } | Custom rotation in degrees applied after basic orientation |
| faceCamera | boolean | true | Orient the object toward the camera's position. |
Events
| Event | Properties | Description |
|---|---|---|
| object-placed | { entity, position, orientation } | Fired when an object is successfully placed |
How Object Orientation Works
Understanding how the orientation properties work together is crucial for achieving the desired placement:
The Placement Process
When an object is placed, the following sequence occurs:
- The object's position is set to the hit point on the surface
- The object's rotation is reset to identity (zero rotation)
- If
adjustOrientationis true:- The surface type is detected (floor, wall, ceiling)
- Basic orientation is applied based on surface type
- If
faceCamerais true, additional rotation is applied to face the camera
- If
adjustOrientationis false butfaceCamerais true:- The object is rotated to face the camera directly
- Custom rotation is applied from the
customRotationproperty - The object is scaled according to the
scaleproperty
Object visibility is optional, but upon placement, visible: true; will be set to the placed object.
Understanding adjustOrientation
The adjustOrientation property determines whether the system should automatically orient the object based on surface type:
| adjustOrientation | Result | When to use |
|---|---|---|
| true | Object orientation is adjusted based on surface type | Most cases - ensures consistent placement across surfaces |
| false | Object maintains its original orientation | When you need complete control over orientation or want the same orientation regardless of surface |
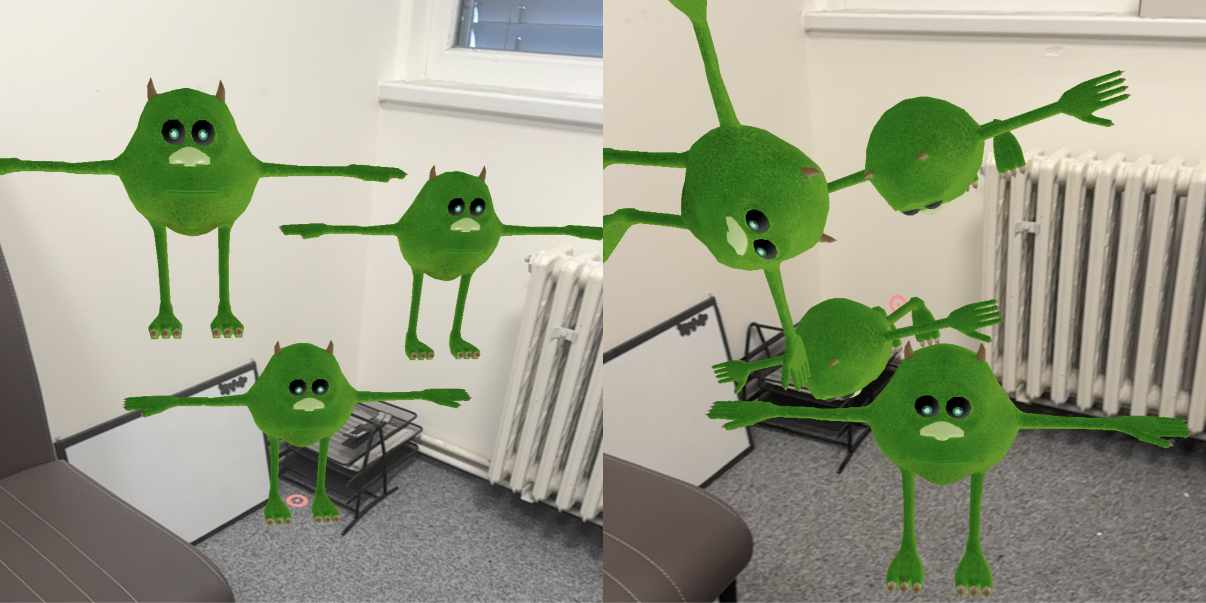 Left: adjustOrientation: false
Left: adjustOrientation: false Right: adjustOrientation: true
Understanding faceCamera
The faceCamera property rotates the object to face the user's viewpoint. If
| Surface Type | faceCamera | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Floor | true | Object rotates around Y-axis to face camera position |
| Wall | true | Object rotates to face camera while maintaining "standing" orientation - if text is present, it stays readible |
| Ceiling | true | Object rotates around Y-axis to face camera position |
When adjustOrientation is false, faceCamera simply rotates the object around its Y-axis to face the camera.
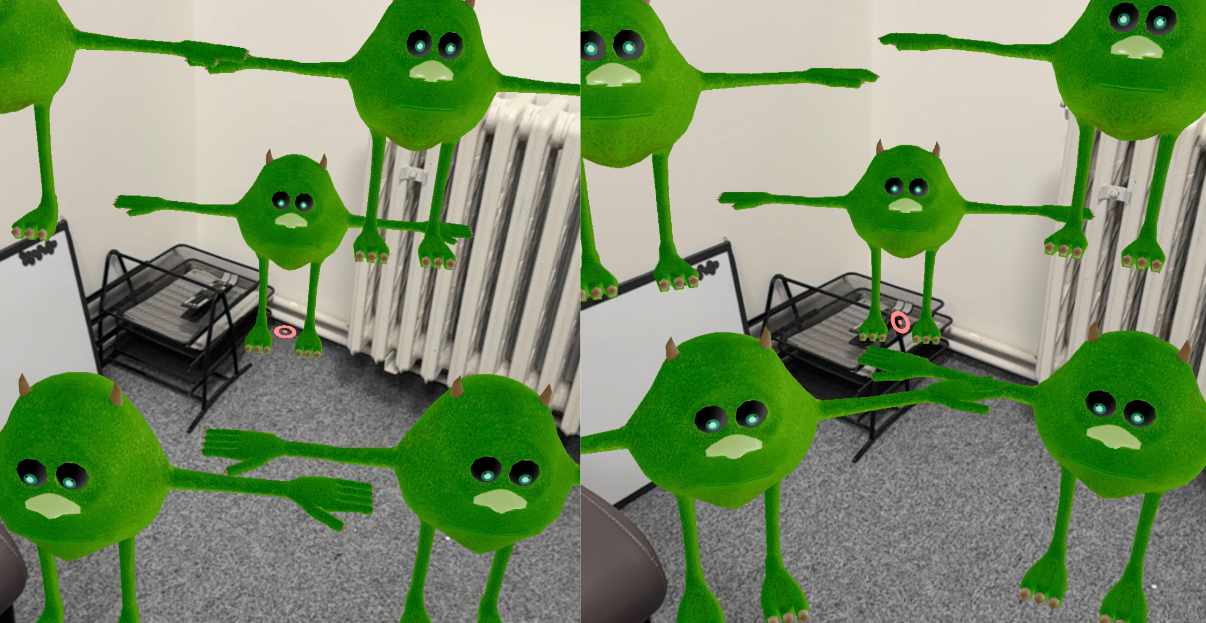 Left: faceCamera: false
Left: faceCamera: false Right: faceCamera: true
Understanding customRotation
The customRotation property applies additional rotation (in degrees) after all other orientation adjustments:
- Rotation is applied in X, Y, Z order
- Values are in degrees (not radians)
- Rotation is relative to the object's current orientation after all other adjustments
- Useful for fine-tuning orientation or creating intentionally angled placements
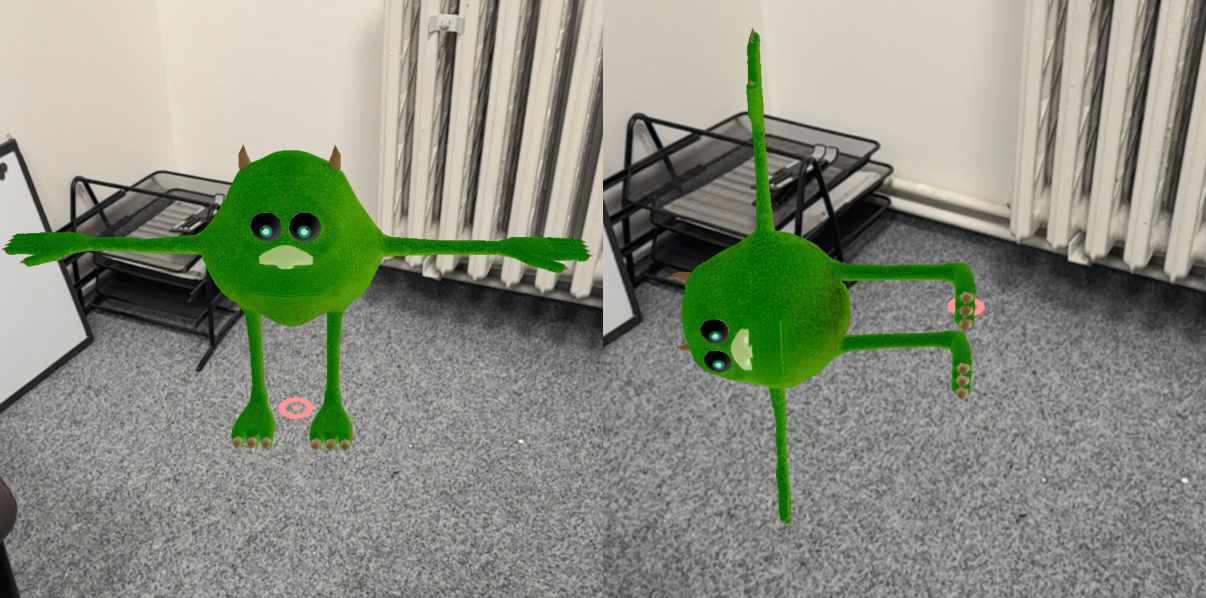 Left: customRotation: 0, 0, 0
Left: customRotation: 0, 0, 0 Right: customRotation: 0, 0, 90
Usage Examples
Standard 3D Model Placement
html
<a-entity
id="chair-model"
gltf-model="#chair"
place-object="
surfaceTypes: horizontal;
adjustOrientation: true;
faceCamera: true"
visible="false">
</a-entity>